To identify the cause of a bacterial infection so appropriate treatment can be given
Gram Stain
Seek advice from your doctor if you have an area of inflamed, red or a painful skin, a wound which does not seem to be healing or any other concerns which might lead you to believe you may have a bacterial infection
A skin swab or fluid/pus (if present) from the site of infection
None
-
How is it used?
This is one of the most commonly performed microbiology tests used to identify the cause of an infection. Often, determining whether an infection is caused by an organism that is Gram positive or Gram negative will be sufficient to allow a doctor to prescribe treatment with an appropriate antibiotic while waiting for more specific tests to be completed. Absence or presence of white blood cells in the Gram stain can determine the adequacy of the specimen.
-
When is it requested?
A Gram stain is performed when a bacterial infection is suspected.
-
What does the test result mean?
Determining the Gram status of an organism allows the doctor to select an appropriate antibiotic before culture results are available. Gram stains cannot predict the organism’s identity or susceptibility to antibiotics. Only the culture of the material can supply this information.
-
Is there anything else I should know?
Bacterial infections should not be ignored, even if the symptoms are mild. You should consult your doctor so treatment, if necessary, can begin promptly, and the spread and severity of the disease can be limited. If left untreated, bacterial infections can migrate throughout the body and cause tissue and organ damage.
-
What are the treatment options for bacterial infections?
Antibiotics are the main treatment of bacterial infections.
-
What does the doctor look for on the slide?
In addition to colour, which indicates whether the organism is Gram positive or Gram negative, the shape of the organism (such as rod-shaped) and the formation of groups of organisms is informative. For example, staphylococcus (staph) bacteria are found in clusters while streptococcus (strep) bacteria are found in chains.
-
What happens if my doctor needs more information than the Gram stain provides?
-
Can I perform this test at home?
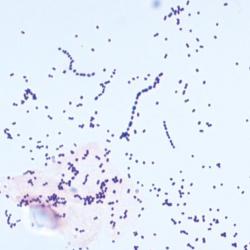
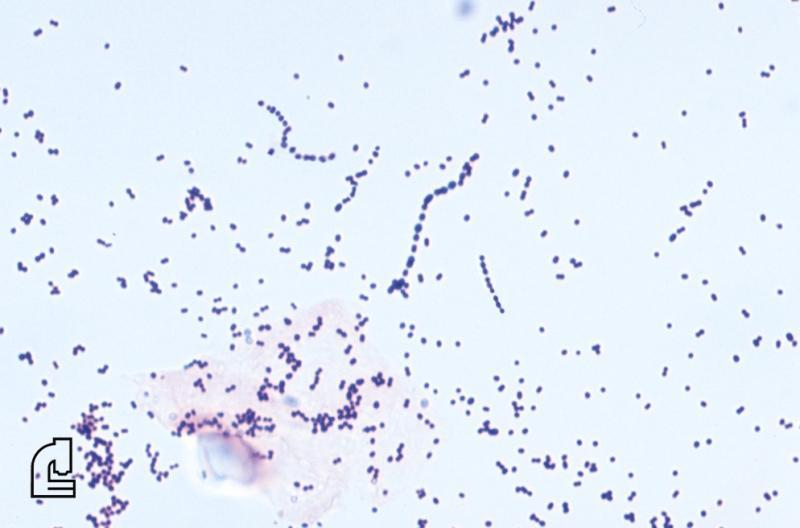
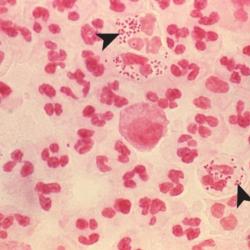
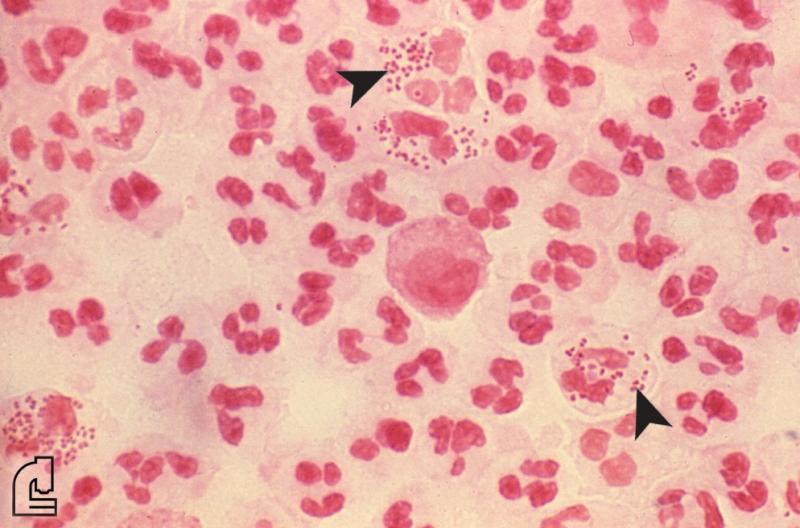
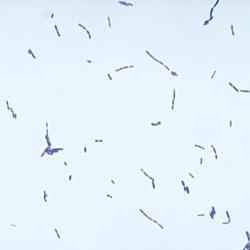
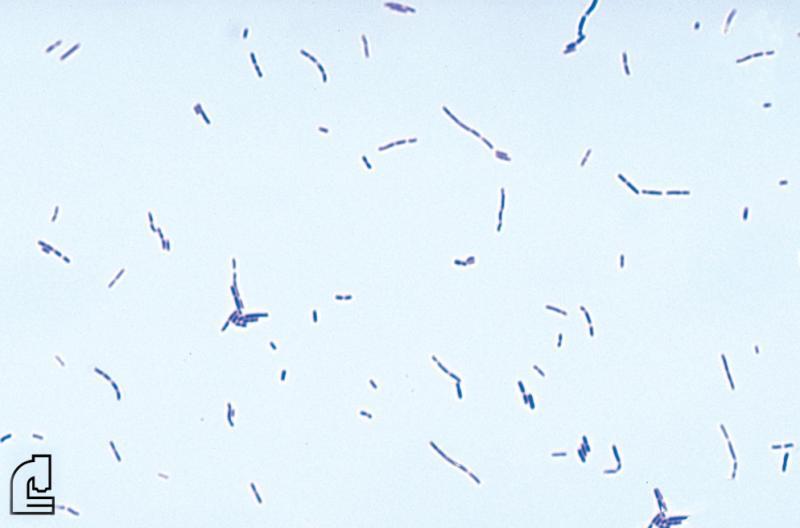
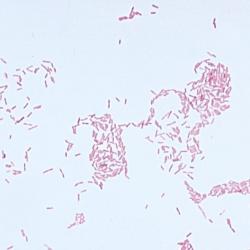
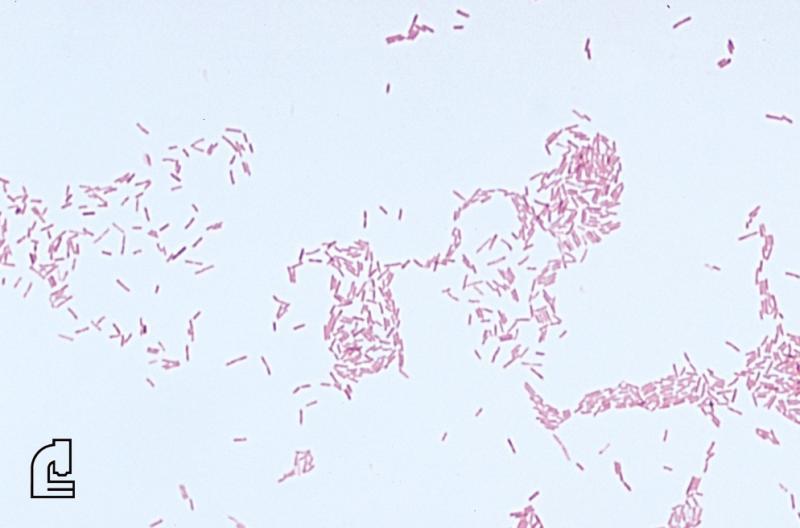
The Gram stain involves applying a sample from an infected area or a sample of bacteria grown in culture onto a glass slide. The slide is then treated with a special stain and examined under a microscope by a trained laboratorian. The color and shape of the bacteria help classify which general types of bacteria are present.
Images used with permission of American Academy of Family Physicians-PT